Testing EC2 Spot Instance Interruptions for Stability
When using EC2 Spot Instances in AWS EKS, you may be concerned about application stability during spot interruptions. This guide demonstrates how to test the resilience of your web services when spot instance interruptions occur within CloudPilot AI, ensuring that your applications can handle these events gracefully.
Prerequisites
Before starting this testing procedure, ensure you have:
- CloudPilot AI is installed in an AWS EKS cluster with spot instances enabled
kubectlconfigured to access your cluster- Access to AWS Fault Injection Simulator (FIS)
Overview
This testing methodology involves deploying a sample nginx application with multiple replicas(You can scale it to 1) and using a load testing tool to generate concurrent requests while simulating spot instance interruptions. The goal is to verify that your application maintains service availability and responds correctly during interruption events.
The testing setup includes:
- Test Application: An nginx deployment with configurable replicas
- Load Testing Tool: A concurrency testing program to generate continuous requests
- Interruption Simulation: AWS FIS to trigger spot instance interruptions
- Monitoring: Real-time response monitoring to validate service stability
Deploy Test Applications
1. Deploy the Test Web Service
Create the nginx deployment and service using the following configuration:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.27-alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 64Mi
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 128Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP2. Deploy the Load Testing Tool
Deploy the concurrency testing program that will generate continuous requests:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hey
labels:
app: hey
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hey
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hey
spec:
containers:
- name: hey
image: cesign/heypod:v0.0.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["sleep", "infinity"]
resources:
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 64Mi
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 128MiApply both configurations to your cluster:
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f hey-deployment.yamlWait for all pods to be in the Running state before proceeding with the test.
Verify Pod Distribution
Before initiating the interruption test, verify that your nginx pods are distributed across different nodes to ensure effective testing:
kubectl get pods -o wide -l app=nginxExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-658b665857-pt6b8 1/1 Running 0 26m 10.0.0.37 ip-10-0-10-173.us-east-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
nginx-658b665857-sq4nw 1/1 Running 0 18m 10.0.33.33 ip-10-0-42-184.us-east-2.compute.internal <none> <none>CloudPilot AI will automatically schedule the pods to different nodes to ensure stability.
Simulate Spot Instance Interruption
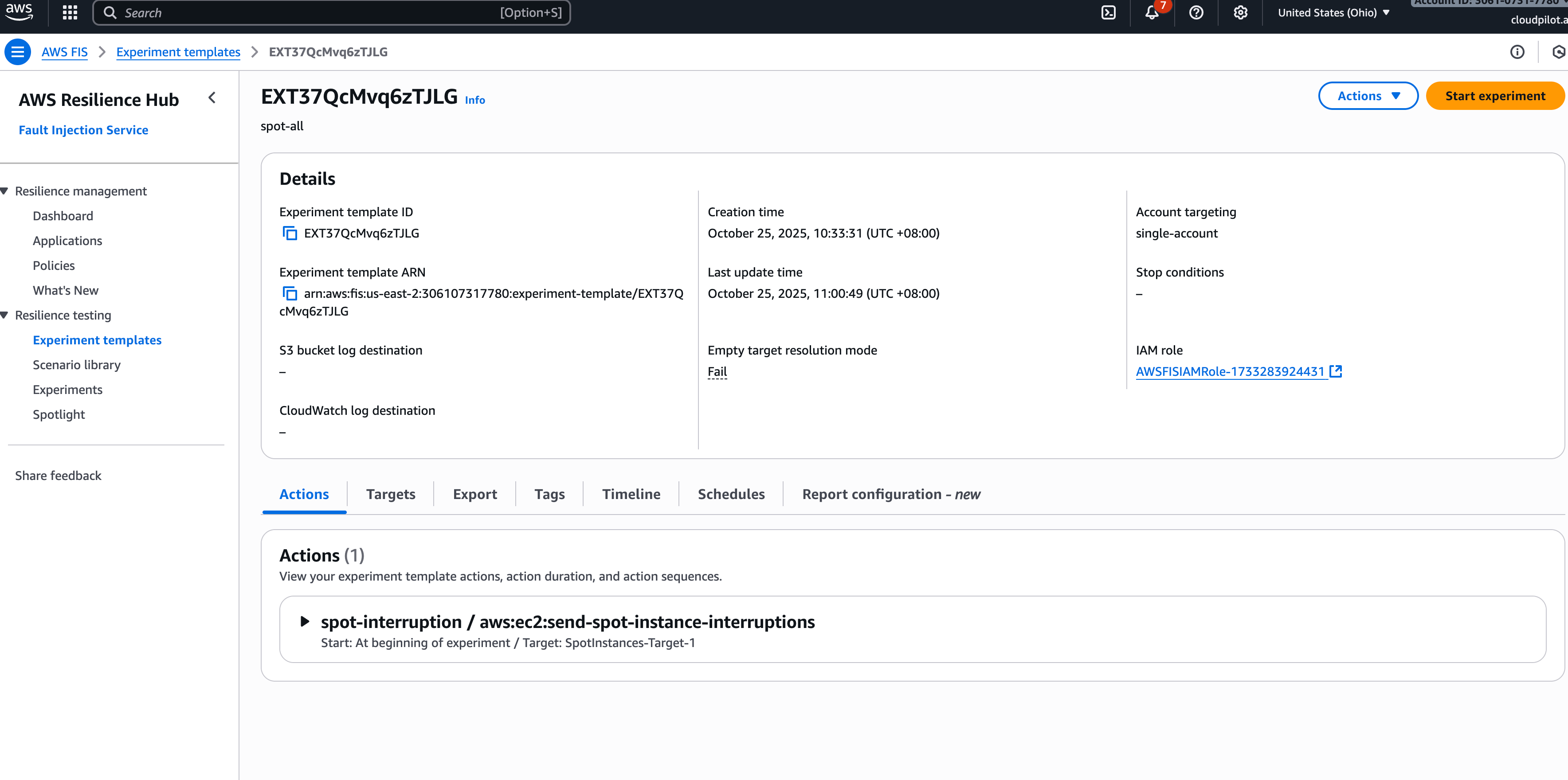
Use AWS Fault Injection Simulator (FIS) to trigger spot instance interruptions on your target nodes:
- Navigate to the AWS FIS console
- Create a new experiment targeting the EC2 instances running your nginx pods
- Configure the spot interruption action
For detailed instructions on setting up spot interruption experiments, refer to the AWS FIS Spot Interruption Tutorial .
Monitor Application Performance During Interruption
1. Start Load Testing
First, identify the load testing pod and execute the concurrency testing tool:
# Get the load testing pod name
kubectl get pods -l app=hey
# Execute the load testing command
kubectl exec <hey-pod-name> -it -- shInside the pod, run the load testing command:
hey -c 10 -z 180s http://nginx.default.svc.cluster.localThis command will:
- Use 10 concurrent workers (
-c 10) - Run for 180 seconds (
-z 180s) - Target the nginx service endpoint
2. Expected Test Results
A successful test run should show results similar to the following:
Summary:
Total: 1.0334 secs
Slowest: 0.0996 secs
Fastest: 0.0003 secs
Average: 0.0082 secs
Requests/sec: 1212.5028
Total data: 770595 bytes
Size/request: 615 bytes
Response time histogram:
0.000 [1] |
0.010 [1117] |■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
0.020 [30] |■
0.030 [5] |
0.040 [0] |
0.050 [0] |
0.060 [0] |
0.070 [0] |
0.080 [46] |■■
0.090 [36] |■
0.100 [18] |■
Latency distribution:
10% in 0.0006 secs
25% in 0.0012 secs
50% in 0.0013 secs
75% in 0.0015 secs
90% in 0.0162 secs
95% in 0.0791 secs
99% in 0.0902 secs
Details (average, fastest, slowest):
DNS+dialup: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0060 secs
DNS-lookup: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0046 secs
req write: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0002 secs
resp wait: 0.0079 secs, 0.0002 secs, 0.0995 secs
resp read: 0.0002 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0898 secs
Status code distribution:
[200] 1253 responses3. Analyze Results
Success Criteria:
- All responses return HTTP status code 200
- Service remains available throughout the test duration
If all responses show status code 200, your application successfully handled the spot instance interruption without service degradation.
Conclusion
CloudPilot AI implements advanced mechanisms to ensure application stability during spot instance interruptions. For more information about our spot instance optimization strategies, visit our blog post on CloudPilot AI .