Overview
The Workload Autoscaler component automatically works in tandem with our Node Autoscaler, dynamically adjusting the requests and limits of all your workloads — scaling them up or down as needed. This ensures that both your workloads and your cluster operate at the optimal balance between performance and cost.
It continuously reduces unnecessary expenses, boosts workload performance, and frees your team from the burden of manual resource tuning — allowing you to focus on innovation and creating real business value.
How It Works
At a high level, Workload Autoscaler runs as a continuous optimization loop:
- It collects workload, Pod, container, and runtime signals from Kubernetes metrics and
cloudpilot-node-agent. - It uses RecommendationPolicy to turn those signals into CPU and Memory recommendations.
- It uses AutoscalingPolicy to decide which workloads should use which recommendation strategy.
- It applies changes according to UpdateMode, UpdateSchedule, DriftThresholds, and the global update limiter.
By default, Workload Autoscaler can start collecting signals and generating recommendations before you enable proactive updates. This lets you observe behavior first, then gradually turn on active optimization for selected workloads.
Optimization Rate Control
We provide multi-dimensional rate-control mechanisms for proactively optimizing (Evict & ReCreate) workloads:
- Update Time Window: You can configure the Workload Autoscaler to apply different optimization behaviors during specific time windows. For example, you may choose to use OnCreate update mode (apply recommendations only when Pods are created) from Monday to Friday, 08:00–20:00, and switch to InPlace update mode (allowing automatic application of updated recommendations to running Pods) during all other hours. For detailed configuration, see here.
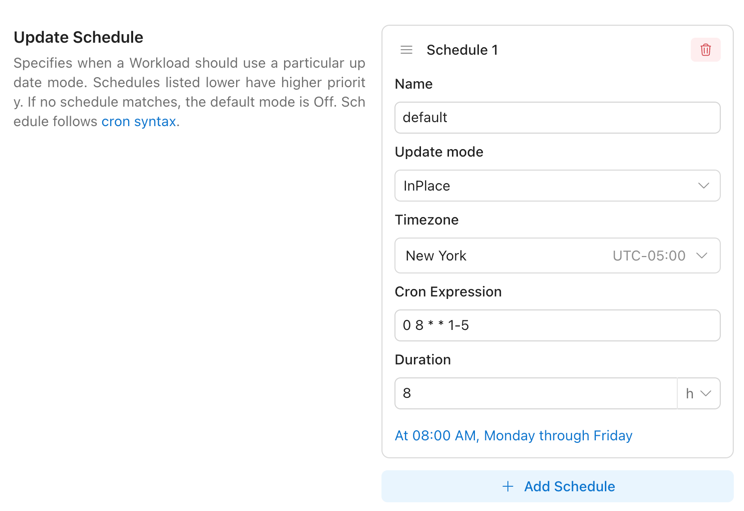
- Global Update Rate Control: You can configure a global environment variable to control how many proactive update operations the Workload Autoscaler is allowed to perform within each time window. For detailed configuration, see here.
| ENV var | Default | What it controls |
|---|---|---|
LIMITER_QUOTA_PER_WINDOW | 5 | Tokens added to the bucket each window. |
LIMITER_BURST | 10 | Maximum tokens allowed in the bucket (peak operations within a window). |
LIMITER_WINDOW_SECONDS | 30 | Window length in seconds; every window adds LIMITER_QUOTA_PER_WINDOW tokens. |
- Gradually Enable Workload Optimization: After connecting your cluster, you can progressively enable proactive optimization for each workload. This allows you to safely and controllably bring all workloads under the management of the Workload Autoscaler.
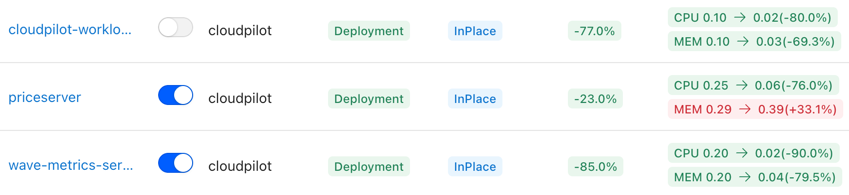
- Drift Control: You can configure DriftThresholds in the AutoscalingPolicy. DriftThresholds define how much deviation is allowed between the recommended values and the current resource configuration before an optimization action is triggered.

Visualization
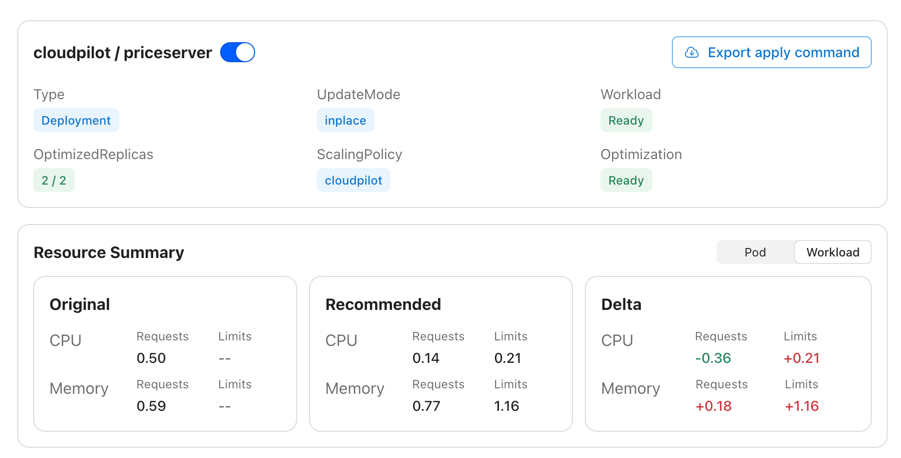
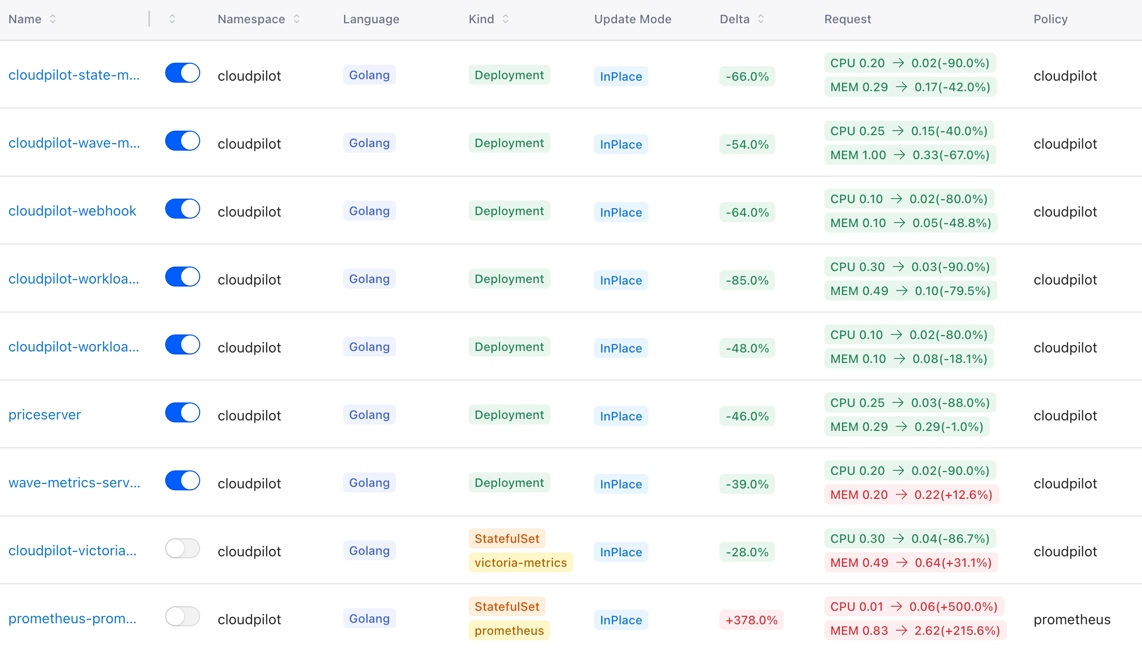
Most existing open-source VPA solutions fail to provide a high-quality visualization interface, leaving users unable to clearly understand the value that VPA brings to a specific workload or to the entire cluster. CloudPilot AI addresses this gap by offering a powerful visual dashboard that helps you easily track each workload’s resource usage and the historical changes of its recommendations.
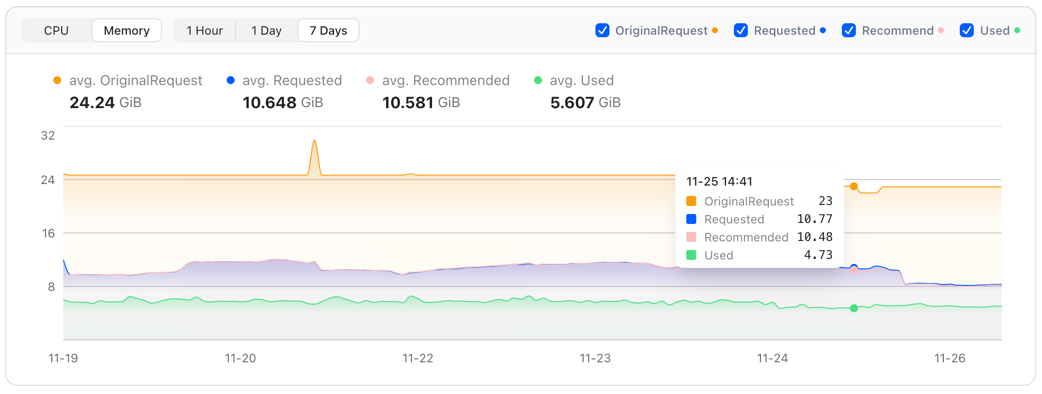
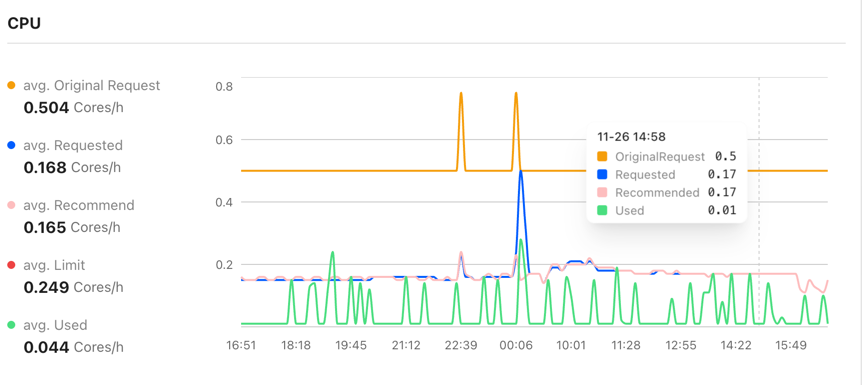
In addition, you can examine optimization details from both the Pod and Workload perspectives, including recommendation history and real resource usage trends.
Flexible Recommendation Settings
In most existing VPA-style products, users can configure only a limited subset of the key variables that influence recommendations. CloudPilot AI aims to maximize the number of workload types that can be optimized, so we expose almost all configuration options.
By defining a RecommendationPolicy, you can flexibly control how recommendations are calculated — including Buffer, History Window, Resource Limits, Evaluation Period, and more. For detailed configuration instructions, see here.
For Java workloads, RecommendationPolicy also supports JVM-specific recommendation settings so you can tune how Heap-related recommendations are generated.
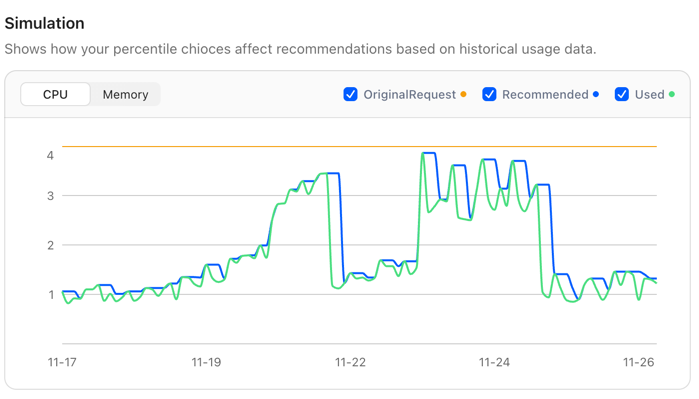
At the same time, we recognize that users may not fully understand the impact of each setting. To address this, CloudPilot AI provides a Simulation feature that visually demonstrates how changes to each configuration parameter affect the final recommendation, helping users better understand the meaning and effect of each option.
Better Limit Management
Beyond adjusting workload Requests, CloudPilot AI also supports adjusting Limits. Limit adjustments are more serious because they directly impact Pod stability and cluster-level resource allocation. To give you finer control, CloudPilot AI allows you to configure how Limits should behave through the AutoscalingPolicy.
We currently support four LimitPolicy modes:
- Remove all Limits
- Keep Limits unchanged
- Maintain a proportional relationship with Requests
- Auto only adjusts Limits when the recommended value is higher than the original Limits.
For detailed configuration, see here.
InPlace Update Support
InPlace Update allows updating workload Requests/Limits without recreating Pods, minimizing the impact on running applications. This feature officially entered Beta in Kubernetes v1.33 and is enabled by default.
However, InPlace Update still comes with several limitations. For example:
- It disallows operations that would change a Pod’s QoS class
- Memory Limits cannot be decreased
- Other API-level validation constraints
CloudPilot AI provides enhanced and safer support for InPlace Update inside the Workload Autoscaler. It can detect common failure scenarios such as QoS class conflicts, unsupported Memory limit changes, and PodResizePending, then handle them with fallback-aware behavior.
More details are available here.
Configure Everything in 3 Minutes
We understand the pain of configuring hundreds of workloads individually. That’s why CloudPilot AI offers an extremely simple setup process—just 3 minutes to fully configure workload optimization across your entire cluster.
By default, CloudPilot AI provides:
- 3 built-in RecommendationPolicies
- A default AutoscalingPolicy
You simply choose the RecommendationPolicy that suits your workloads, then use AutoscalingPolicy to select which workloads should be optimized.
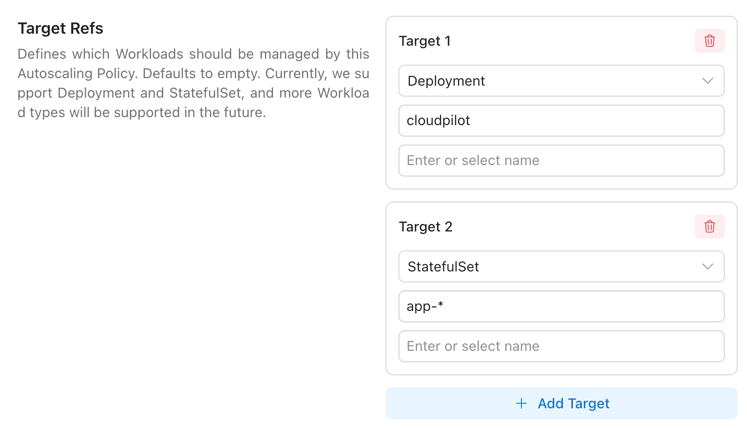
We support selecting workloads flexibly via WorkloadKind, Namespace, Name wildcards, and LabelSelector. See details here.
You may define multiple AutoscalingPolicies to map different workloads to different optimization strategies. You can even rely on a single default AutoscalingPolicy to target all workloads, and then override specific workloads using Policies with higher Priority.
This makes it easy to apply one policy to Java workloads and another to non-Java workloads, or to split policies by environment, team, or application type.
Java Workload Optimization
Optimizing Java workloads in Kubernetes is notoriously challenging. Java applications often size their internal memory regions and tune garbage collection behavior based on the resources available at startup. As a result, dynamically changing Requests and Limits at runtime may not be correctly reflected by the JVM, potentially leading to performance regressions or stability issues.
This JVM-specific behavior also makes traditional resource tuning approaches less effective. For example, the memory usage observed by tools like VPA does not necessarily reflect the JVM’s actual memory pressure or allocation behavior, which makes accurate recommendations difficult.
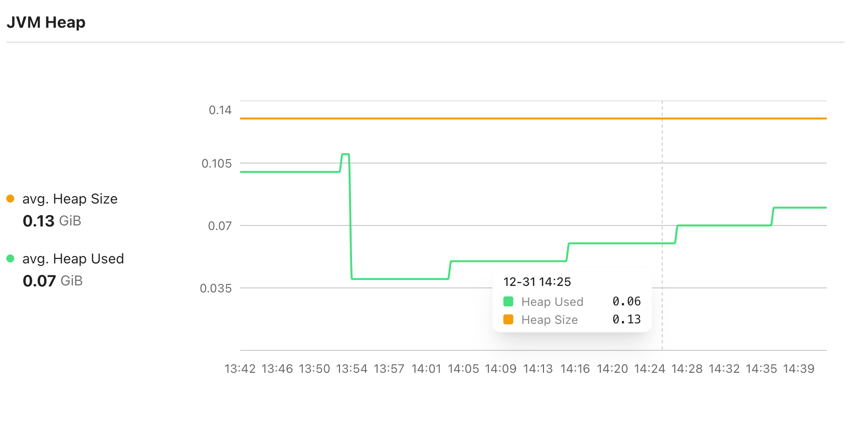
CloudPilot AI addresses this by introducing specialized handling for Java workloads in Workload Autoscaler. We use eBPF to automatically collect JVM-level metrics across the cluster. By analyzing signals such as heap_used/heap_size and gc_duration, we can more accurately assess resource demand and continuously optimize Java workloads—monitoring GC behavior, CPU throttling, and other runtime signals to balance both performance and cost.
You can also combine this with JVM-specific settings in RecommendationPolicy when you need finer control over Heap-related recommendation behavior.
See details here.
Runtime Language / Application Type Autodetection and Specialized Handling
CloudPilot AI can now automatically detect each workload’s runtime language and application type by collecting and analyzing container runtime signals via eBPF.
Supported Runtime Languages
We currently detect and support:
- Java
- Golang
- Node.js
- Python
- .NET
- Ruby
- PHP
Supported Application Types
We also identify 60+ common Kubernetes application types, including (but not limited to):
- mongodb
- redis
- zookeeper
- nginx
- kafka
- opensearch
With both runtime language and application type identified, Workload Autoscaler can apply specialized optimization strategies tailored to different workload characteristics, improving the trade-off between stability and cost. These runtime-derived labels can also be used by AutoscalingPolicy to target different workload groups more precisely.
Workload Resource Startup Boost
We’ve observed that many workloads—especially Java workloads—often require multiple times more resources during startup than during steady-state operation. We call this the Startup Spike problem.
Traditionally, users face a painful trade-off:
- Configure high static Requests to satisfy startup needs → wastes resources during steady state
- Configure low Requests to save cost → increases the risk of startup failures and cascading instability (often involving node scheduling and resource contention)
CloudPilot AI introduces Startup Boost in Workload Autoscaler to explicitly separate startup resource demand from runtime resource demand.
Startup Boost temporarily increases a workload’s Requests and Limits during startup, then automatically scales them back to appropriate steady-state values once the workload becomes ready—eliminating chronic over-provisioning without sacrificing reliability.
Startup Boost is designed for InPlace-based update flows. For Memory, it boosts Requests during startup but does not raise Limits.
Learn more about ResourceStartupBoost here: ResourceStartupBoost

Supported Workload Types
CloudPilot AI Workload Autoscaler supports optimization for the following Kubernetes workload types:
| Workload Type | Supported | Supported Update Modes |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Yes | OnCreate, ReCreate, InPlace |
| StatefulSet | Yes | OnCreate, ReCreate, InPlace |
| DaemonSet | In Progress | OnCreate, InPlace |
| Rollout | In Progress | OnCreate, ReCreate, InPlace |
RoadMap
You can view the planned features for upcoming versions of the Workload Autoscaler here.